Your Treatment resistant schizophrenia definition images are ready. Treatment resistant schizophrenia definition are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Treatment resistant schizophrenia definition files here. Find and Download all royalty-free images.
If you’re searching for treatment resistant schizophrenia definition images information linked to the treatment resistant schizophrenia definition interest, you have come to the ideal blog. Our site frequently provides you with suggestions for viewing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more informative video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
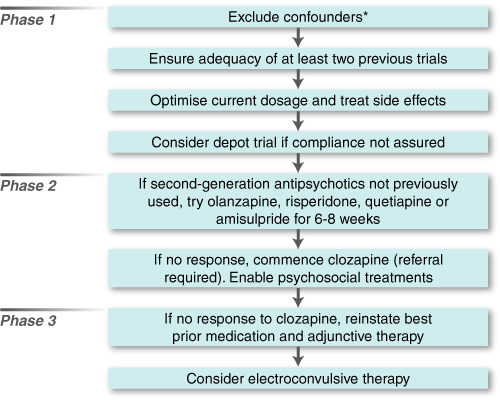
Treatment Resistant Schizophrenia Definition. 2 adequate pharmacological treatment. And 3 persistence of significant symptoms despite this treatment. At present a uniform definition of treatment resistance in the pharmacotherapy of schizophrenia is not available2 Most treatment guidelines require the failure of at least two antipsychotic trials with different compounds including at least one second-generation antipsychotic in adequate dose over a period between 2 and 8 weeks before treatment. Treatment resistance in schizophrenia is a fairly common problem faced by psychiatrists worldwide.

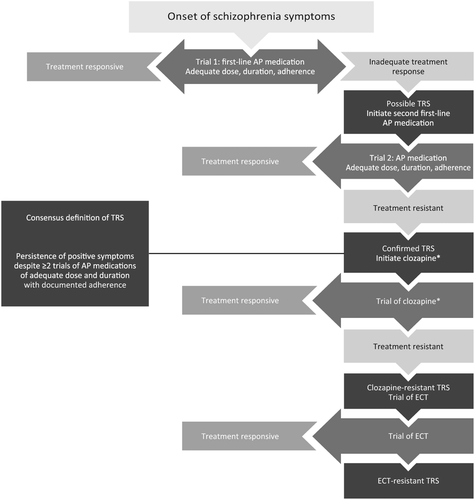
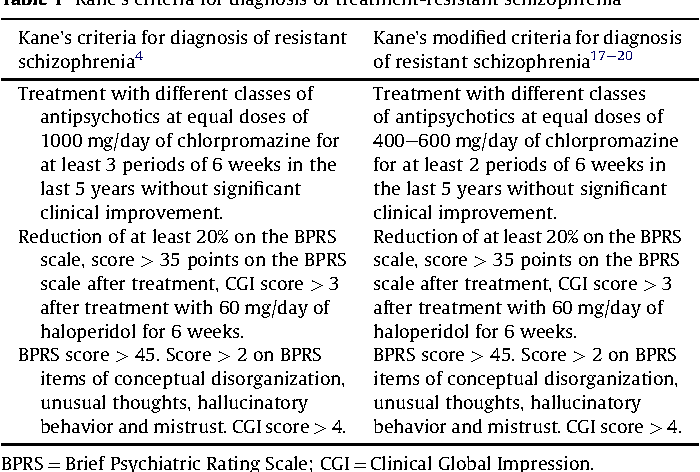
Treatment-resistant schizophrenia TRS represents a major clinical challenge. 1 a confirmed diagnosis of schizophrenia based on validated criteria. Treatment resistance in schizophrenia is a fairly common problem faced by psychiatrists worldwide. Three key elements define the concept of treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Brenner and Merlo 3 proposed that treatment-resistant schizophrenia be considered at one end of a spectrum of antipsychotic drug response rather than being clearly differentiated from treatment-responsive schizophrenia. At present a uniform definition of treatment resistance in the pharmacotherapy of schizophrenia is not available2 Most treatment guidelines require the failure of at least two antipsychotic trials with different compounds including at least one second-generation antipsychotic in adequate dose over a period between 2 and 8 weeks before treatment.
Treatment-resistant schizophrenia TRS represents a major clinical challenge.
An inadequate response need not be restricted to the persistence of positive symptoms but this is the most common definition. Patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia can be broadly defined to include any persons with residual symptoms that cause distress or impairment despite several treatment attempts. The most common definition of treatment-resistant schizophrenia denotes patients with schizophrenia who despite at least two adequate trials of classical neuroleptic drugs have persistent moderate to severe positive or disorganisation or negative symptoms together with poor social and work function over a prolonged period of time. Treatment Resistant Schizophrenia General Principles Treatment resistant schizophrenia TRS is defined by an inadequate response to a succession of treatments Taylor and Duncan-McConnell 2000. Unfortunately this definition may include most of our patients with schizophrenia. Patients with treatment resistant schizophrenia TRS are 3-11-fold higher compared to patients with schizophrenia in general Kennedy et al.
 Source: mja.com.au
Source: mja.com.au
1 a confirmed diagnosis of schizophrenia based on validated criteria 2 adequate pharmacological treatment and 3 persistence of significant symptoms despite adequate treatment. 1 a confirmed diagnosis of schizophrenia based on validated criteria. 1 a confirmed diagnosis of schizophrenia based on validated criteria 2 adequate pharmacological treatment and 3 persistence of significant symptoms despite adequate treatment. An inadequate response need not be restricted to the persistence of positive symptoms but this is the most common definition. Treatment-resistant schizophrenia is a phenomenon that most clinicians and researchers try to combat in their daily practices.
 Source: focus.psychiatryonline.org
Source: focus.psychiatryonline.org
The most common definition of treatment-resistant schizophrenia denotes patients with schizophrenia who despite at least two adequate trials of classical neuroleptic drugs have persistent moderate to severe positive or disorganisation or negative symptoms together with poor social and work function over a prolonged period of time. 2 The static failure to respond to treatment suggests that schizophrenia is a heterogeneous. Defining treatment-resistant schizophrenia TRS like those of Kane 4 Dencker and al 5 and Brenner and al 6 some studies have subsequently estimated its prevalence. The large number and variety of risk factors associated with poor prognosis or poor response. 1 a confirmed diagnosis of schizophrenia based on validated criteria.

The most common definition of treatment-resistant schizophrenia denotes patients with schizophrenia who despite at least two adequate trials of classical neuroleptic drugs have persistent moderate to severe positive or disorganisation or negative symptoms together with poor social and work function over a prolonged period of time. 2 The static failure to respond to treatment suggests that schizophrenia is a heterogeneous. 2014 and they often have long hospitalizations Hasan et al. Patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia can be broadly defined to include any persons with residual symptoms that cause distress or impairment despite several treatment attempts. Three key elements define the concept of treatment resistant schizophrenia.

Patients with treatment resistant schizophrenia TRS are 3-11-fold higher compared to patients with schizophrenia in general Kennedy et al. Treatment-resistant schizophrenia TRS has been defined mainly by severity of positive symptoms and response to antipsychotics derived from a relative change in the representative scales most frequently 20 decrease in the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale. 2 The static failure to respond to treatment suggests that schizophrenia is a heterogeneous. PANSS but these definitions have not necessarily been consistent. No particular psychopathology of schizophrenia specifically suggests treatment-resistant disease.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
At present a uniform definition of treatment resistance in the pharmacotherapy of schizophrenia is not available2 Most treatment guidelines require the failure of at least two antipsychotic trials with different compounds including at least one second-generation antipsychotic in adequate dose over a period between 2 and 8 weeks before treatment. Patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia can be broadly defined to include any persons with residual symptoms that cause distress or impairment despite several treatment attempts. Patients with treatment resistant schizophrenia TRS are 3-11-fold higher compared to patients with schizophrenia in general Kennedy et al. The label treatment resistance is used particularly to refer to patients whose positive symptoms of schizophrenia including delusions and hallucinations have not responded to treatment1-3 For definitions of positive and negative symptoms see Lambert and Castle 4 The focus on positive symptoms has arisen largely because other domains were either not. Unfortunately this definition may include most of our patients with schizophrenia.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The large number and variety of risk factors associated with poor prognosis or poor response. And 3 persistence of significant symptoms despite this treatment. The most common definition of treatment-resistant schizophrenia denotes patients with schizophrenia who despite at least two adequate trials of classical neuroleptic drugs have persistent moderate to severe positive or disorganisation or negative symptoms together with poor social and work function over a prolonged period of time. Unfortunately this definition may include most of our patients with schizophrenia. Patients with treatment resistant schizophrenia TRS are 3-11-fold higher compared to patients with schizophrenia in general Kennedy et al.
 Source: scielo.br
Source: scielo.br
Patients with treatment resistant schizophrenia TRS are 3-11-fold higher compared to patients with schizophrenia in general Kennedy et al. A lthough antipsychotic medications have been the mainstay of treatment for schizophrenia approximately one-third of individuals with schizophrenia show a limited response to antipsychotic treatment 1 which has led to the term treatment-resistant schizophrenia TRS. Treatment-resistant schizophrenia TRS represents a major clinical challenge. Brenner and Merlo 3 proposed that treatment-resistant schizophrenia be considered at one end of a spectrum of antipsychotic drug response rather than being clearly differentiated from treatment-responsive schizophrenia. An inadequate response need not be restricted to the persistence of positive symptoms but this is the most common definition.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Atients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia can be broadly defined to include any persons with residual symptoms that cause distress or impairment despite several treatment at- tempts. Patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia can be broadly defined to include any persons with residual symptoms that cause distress or impairment despite several treatment attempts. Treatment-resistant schizophrenics are patients who are repeatedly admitted to hospitals or require frequent visits to specialists or as study subjects are often excluded from participation in efficacy and safety studies of new. PANSS but these definitions have not necessarily been consistentIntegrating past evidence and real. 2014 and they often have long hospitalizations Hasan et al.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Treatment-resistant schizophrenics are patients who are repeatedly admitted to hospitals or require frequent visits to specialists or as study subjects are often excluded from participation in efficacy and safety studies of new. Unfortunately this definition may include most of our patients with schizophrenia. Treatment resistance represents the greatest unmet need in schizophrenia care Nakajima et al. Patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia can be broadly defined to include any persons with residual symptoms that cause distress or impairment despite several treatment attempts. Although clozapine has established efficacy for treatment-resistant schizophrenia and is indicated for this purpose it would be ideal if.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Treatment-resistant schizophrenia TRS represents a major clinical challenge. Three key elements define the concept of treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Regarding the definitions of TRS an international leadership in schizophrenia work group called Treatment Response and Resistance in Psychosis TRRIP conducted a comprehensive review of all historical definitions and clinical trial definitions of TRS They found that over half of the clinical trials had inadequate. Treatment-resistant schizophrenics are patients who are repeatedly admitted to hospitals or require frequent visits to specialists or as study subjects are often excluded from participation in efficacy and safety studies of new. Unfortunately this definition may include most of our patients with schizophrenia.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Unfortunately this definition may include most of our patients with schizophrenia. Treatment-resistant schizophrenia TRS represents a major clinical challenge. The large number and variety of risk factors associated with poor prognosis or poor response. While many definitions of TRS include failure of two different antipsychotics as a minimum criterion the wide variability in inclusion criteria has challenged the consistency and reproducibility of results. Unfortunately this definition may include most of our patients with schizophrenia.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
1 a confirmed diagnosis of schizophrenia based on validated criteria. Three key elements define the concept of treatment resistant schizophrenia. No particular psychopathology of schizophrenia specifically suggests treatment-resistant disease. And 3 persistence of significant symptoms despite this treatment. Patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia can be broadly defined to include any persons with residual symptoms that cause distress or impairment despite several treatment attempts.
 Source: psychiatrictimes.com
Source: psychiatrictimes.com
The concept and definition of Treatment Resistant Schizophrenia TRS is still far from satisfactory. Patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia can be broadly defined to include any persons with residual symptoms that cause distress or impairment despite several treatment attempts. Treatment-resistant schizophrenia TRS represents a major clinical challenge. The large number and variety of risk factors associated with poor prognosis or poor response. A Reaffirmation and Extension.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Treatment resistant schizophrenia TRS refers to the significant proportion of schizophrenia patients who continue to have symptoms and poor outcomes despite treatment. At present a uniform definition of treatment resistance in the pharmacotherapy of schizophrenia is not available2 Most treatment guidelines require the failure of at least two antipsychotic trials with different compounds including at least one second-generation antipsychotic in adequate dose over a period between 2 and 8 weeks before treatment. Unfortunately this definition may include most of our patients with schizophrenia. And 3 persistence of significant symptoms despite this treatment. Three key elements define the concept of treatment resistant schizophrenia.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Treatment-resistant schizophrenics are patients who are repeatedly admitted to hospitals or require frequent visits to specialists or as study subjects are often excluded from participation in efficacy and safety studies of new. Treatment-resistant schizophrenia is a phenomenon that most clinicians and researchers try to combat in their daily practices. Treatment-resistant schizophrenia TRS represents a major clinical challenge. The concept and definition of Treatment Resistant Schizophrenia TRS is still far from satisfactory. 2 The static failure to respond to treatment suggests that schizophrenia is a heterogeneous.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
A lthough antipsychotic medications have been the mainstay of treatment for schizophrenia approximately one-third of individuals with schizophrenia show a limited response to antipsychotic treatment 1 which has led to the term treatment-resistant schizophrenia TRS. Although clozapine has established efficacy for treatment-resistant schizophrenia and is indicated for this purpose it would be ideal if. Treatment Resistant Schizophrenia General Principles Treatment resistant schizophrenia TRS is defined by an inadequate response to a succession of treatments Taylor and Duncan-McConnell 2000. PANSS but these definitions have not necessarily been consistent. The large number and variety of risk factors associated with poor prognosis or poor response.
 Source: aafp.org
Source: aafp.org
Atients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia can be broadly defined to include any persons with residual symptoms that cause distress or impairment despite several treatment at- tempts. Patients with treatment resistant schizophrenia TRS are 3-11-fold higher compared to patients with schizophrenia in general Kennedy et al. 1 a confirmed diagnosis of schizophrenia based on validated criteria 2 adequate pharmacological treatment and 3 persistence of significant symptoms despite adequate treatment. Treatment-resistant schizophrenia TRS represents a major clinical challenge. Treatment resistance in schizophrenia is a fairly common problem faced by psychiatrists worldwide.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Several demographic clinical and neurologic predictors are associated with TRS. Treatment-resistant schizophrenia TRS has been defined mainly by severity of positive symptoms and response to antipsychotics derived from a relative change in the representative scales most frequently 20 decrease in the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale. Treatment-resistant schizophrenia TRS has been defined as the persistence of symptoms despite 2 trials of antipsychotic medications of adequate dose and duration with documented adherence. Regarding the definitions of TRS an international leadership in schizophrenia work group called Treatment Response and Resistance in Psychosis TRRIP conducted a comprehensive review of all historical definitions and clinical trial definitions of TRS They found that over half of the clinical trials had inadequate. PANSS but these definitions have not necessarily been consistent.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title treatment resistant schizophrenia definition by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.