Your Symptoms of treatment resistant schizophrenia images are available. Symptoms of treatment resistant schizophrenia are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Symptoms of treatment resistant schizophrenia files here. Find and Download all royalty-free images.
If you’re searching for symptoms of treatment resistant schizophrenia images information related to the symptoms of treatment resistant schizophrenia keyword, you have pay a visit to the ideal site. Our website always provides you with suggestions for downloading the highest quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video articles and graphics that match your interests.
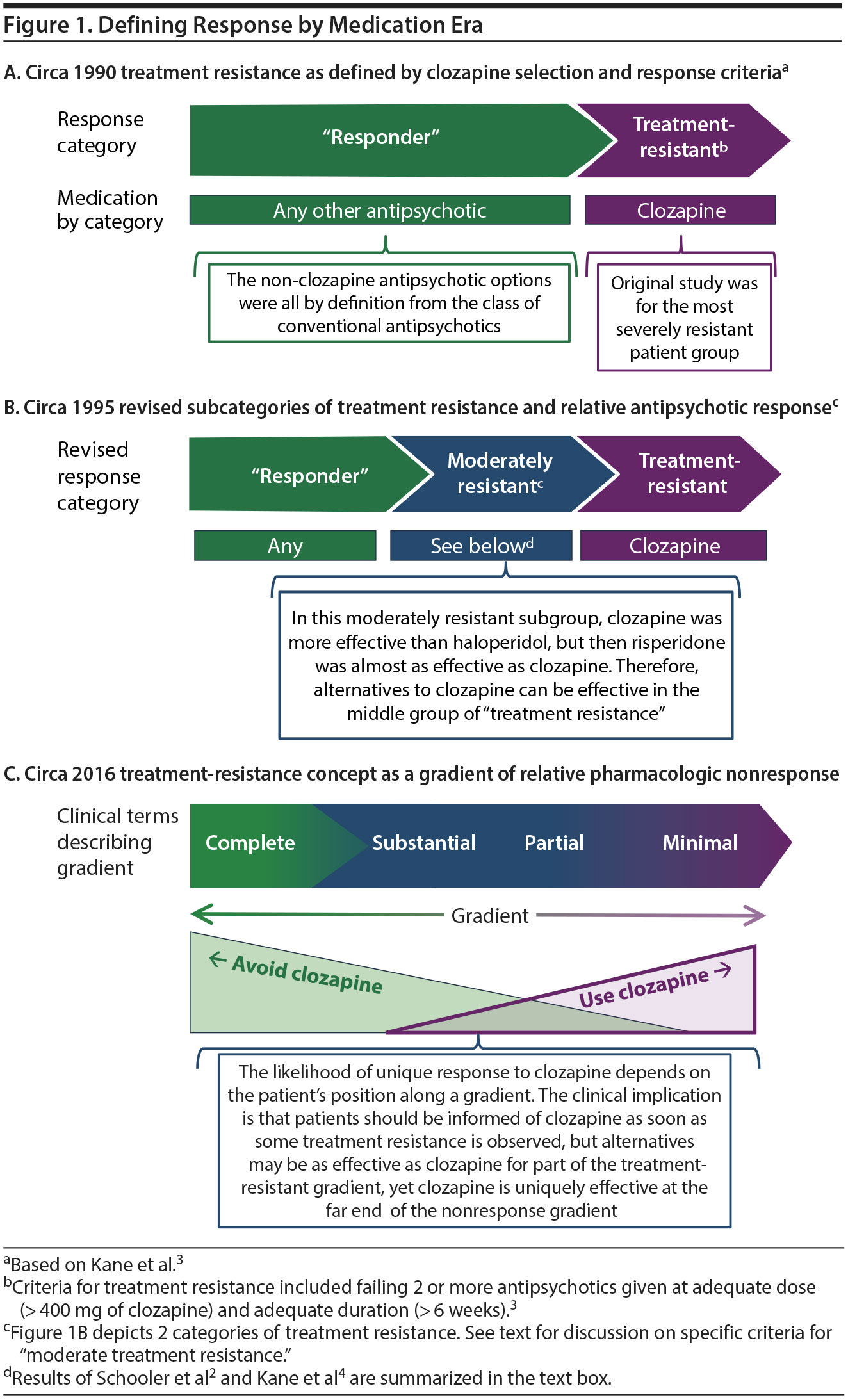
Symptoms Of Treatment Resistant Schizophrenia. The most common definition of treatment-resistant schizophrenia denotes patients with schizophrenia who despite at least two adequate trials of classical neuroleptic drugs have persistent moderate to severe positive or disorganisation or negative symptoms together with poor social and work function over a prolonged period of time. Treatment Resistant Schizophrenia General Principles Treatment resistant schizophrenia TRS is defined by an inadequate response to a succession of treatments Taylor and Duncan-McConnell 2000. Patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia showed a smaller reduction of negative symptoms after active vs sham tDCS. This was a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled.

While many definitions of TRS include failure of two different antipsychotics as a minimum criterion the wide variability in inclusion criteria has challenged the consistency and reproducibility of results from studies of TRS. We adopt a systems-level approach positing a greater role for cognitive control mechanisms in the development of psychotic symptoms and illustrate the clinical application of this via a case report of treatment-resistant patients treated successfully with adjunct pro. At least one of these must be delusions hallucinations or disorganized speech. 1 Positive symptoms include delusions and hallucinations. Patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia showed a smaller reduction of negative symptoms after active vs sham tDCS. There is a phenomenon called burnout in older persons with schizophrenia in which positive symptoms improve or the psychosis burns out but the negative symptoms do not appear to.
2 The static failure to respond to treatment suggests that schizophrenia is a heterogeneous condition with different.
The most common definition of treatment-resistant schizophrenia denotes patients with schizophrenia who despite at least two adequate trials of classical neuroleptic drugs have persistent moderate to severe positive or disorganisation or negative symptoms together with poor social and work function over a prolonged period of time. Treatment-resistant schizophrenia is a serious clinical problem. This was a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled. There is a phenomenon called burnout in older persons with schizophrenia in which positive symptoms improve or the psychosis burns out but the negative symptoms do not appear to. Kraepelinian schizophrenia with severe persistent cognitive deterioration Deficit schizophrenia with prominent primary negative symptoms. 1 No consistent reliable predictor of response has yet been identified.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
This was a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled. Treatment-resistant symptoms complicate the clinical course of schizophrenia and a large proportion of patients do not reach functional recovery. Schizophrenia is a severe mental disorder characterized by positive negative and cognitive symptoms The treatment of schizophrenia was revolutionized by the introduction of chlorpromazine in the 1950s However it rapidly became clear that some patients showed little if any clinical response to treatment with multiple different antipsychotic drugs with the sole exception of clozapine. Serum interleukin IL-6 levels in schizophrenia correlate with the severity of negative symptoms. Similar effects were observed for those with ultratreatment-resistant schizophrenia those who used clozapine and those who took higher haloperidol dose equivalents eTables 4 and 5 in Supplement 2.
 Source: psychopharmacologyinstitute.com
Source: psychopharmacologyinstitute.com
Schizophrenia is a severe mental disorder characterized by positive negative and cognitive symptoms The treatment of schizophrenia was revolutionized by the introduction of chlorpromazine in the 1950s However it rapidly became clear that some patients showed little if any clinical response to treatment with multiple different antipsychotic drugs with the sole exception of clozapine. Negative symptoms are characterised by deficits in normal behaviour which are categorised into five domains. An inadequate response need not be restricted to the persistence of positive symptoms but this is the most common definition. In contrast to treatment-responsive schizophrenia treatment-resistant schizophrenia appears to be characterised by a relatively normal dopamine system but an abnormal glutamate system and significant decreases in grey matter. However according to some authors the definition of resistant schizophrenia must be multidimensional and the field to assess during a clinical trial should be extended and include besides the conventional positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia cognitive deficits quality of life social reintegration occupational impairments and behavioral problems 32-35.
 Source: psychiatrist.com
Source: psychiatrist.com
The label treatment resistance is used particularly to refer to patients whose positive symptoms of schizophrenia including delusions and hallucinations have not responded to treatment1-3 For definitions of positive and negative symptoms see Lambert and Castle 4 The focus on positive symptoms has arisen largely because other domains were either not clinically well recognised or. On a cross-sectional evaluation these patients with chronic schizophrenia were acutely ill and had high symptom levels as defined by a BPRS overall score 45 and an item score of 2 in hallucinations suspiciousness disorganization and unusual thought content. There is a phenomenon called burnout in older persons with schizophrenia in which positive symptoms improve or the psychosis burns out but the negative symptoms do not appear to. However patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia often have persistent negative symptoms and prominent cognitive impairment. Delusions Hallucinations Disorganized speech eg frequent derailment or incoherence Grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior Negative symptoms ie diminished emotional expression or avolition.
 Source: psychiatrictimes.com
Source: psychiatrictimes.com
1 Positive symptoms include delusions and hallucinations. The label treatment resistance is used particularly to refer to patients whose positive symptoms of schizophrenia including delusions and hallucinations have not responded to treatment1-3 For definitions of positive and negative symptoms see Lambert and Castle 4 The focus on positive symptoms has arisen largely because other domains were either not clinically well recognised or. Treatment resistant schizophrenia TRS refers to the significant proportion of schizophrenia patients who continue to have symptoms and poor outcomes despite treatment. This study shows estradiol is an effective and clinically significant adjunctive therapy for women with treatment-resistant schizophrenia particularly for. This study aimed to explore the potential immune mechanism of SSRI augmentation in the management of patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia assessing changes in IL-6 and CRP amounts.
 Source: aafp.org
Source: aafp.org
2 Previous studies suggest a relationship between clozapine plasma concentrations and therapeutic response 34 and a threshold of 350 ngml has often been proposed as necessary to. Blunted affect alogia social withdrawal anhedonia and avolition. On a cross-sectional evaluation these patients with chronic schizophrenia were acutely ill and had high symptom levels as defined by a BPRS overall score 45 and an item score of 2 in hallucinations suspiciousness disorganization and unusual thought content. Delusions Hallucinations Disorganized speech eg frequent derailment or incoherence Grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior Negative symptoms ie diminished emotional expression or avolition. Therefore IPAP suggests 2 forms of treatment-resistant schizophrenia.

Serum interleukin IL-6 levels in schizophrenia correlate with the severity of negative symptoms. This was a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled. Treatment resistant schizophrenia TRS refers to the significant proportion of schizophrenia patients who continue to have symptoms and poor outcomes despite treatment. This study shows estradiol is an effective and clinically significant adjunctive therapy for women with treatment-resistant schizophrenia particularly for. Blunted affect alogia social withdrawal anhedonia and avolition.
 Source: scielo.br
Source: scielo.br
Tentative evidence from a diverse range of research fields supports the idea that treatment-resistance may be a categorically distinct disorder. Treatment-resistant schizophrenia is a serious clinical problem. The label treatment resistance is used particularly to refer to patients whose positive symptoms of schizophrenia including delusions and hallucinations have not responded to treatment1-3 For definitions of positive and negative symptoms see Lambert and Castle 4 The focus on positive symptoms has arisen largely because other domains were either not clinically well recognised or. There is a phenomenon called burnout in older persons with schizophrenia in which positive symptoms improve or the psychosis burns out but the negative symptoms do not appear to. Treatment-resistant schizophrenia TRS is broadly defined in clinical guidelines as an inadequate response in target schizophrenia symptoms often positive symptoms following treatment with two or more antipsychotic treatments of adequate dose and duration 2 6789.
 Source: psychscenehub.com
Source: psychscenehub.com
2 The static failure to respond to treatment suggests that schizophrenia is a heterogeneous condition with different. Clozapine is the most effective antipsychotic in treating refractory schizophrenia but only about 50 of patients respond to treatment. The most common definition of treatment-resistant schizophrenia denotes patients with schizophrenia who despite at least two adequate trials of classical neuroleptic drugs have persistent moderate to severe positive or disorganisation or negative symptoms together with poor social and work function over a prolonged period of time. Patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia showed a smaller reduction of negative symptoms after active vs sham tDCS. In consequence polypharmacy is frequently used in treatment-refractory cases addressing psychotic positive negative and cognitive symptoms treatment-emergent side effects caused by antipsychotics and comorbid depressive or obsessive-compulsive symptoms.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Tentative evidence from a diverse range of research fields supports the idea that treatment-resistance may be a categorically distinct disorder. The most common definition of treatment-resistant schizophrenia denotes patients with schizophrenia who despite at least two adequate trials of classical neuroleptic drugs have persistent moderate to severe positive or disorganisation or negative symptoms together with poor social and work function over a prolonged period of time. Patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia showed a smaller reduction of negative symptoms after active vs sham tDCS. However according to some authors the definition of resistant schizophrenia must be multidimensional and the field to assess during a clinical trial should be extended and include besides the conventional positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia cognitive deficits quality of life social reintegration occupational impairments and behavioral problems 32-35. Treatment-resistant symptoms complicate the clinical course of schizophrenia and a large proportion of patients do not reach functional recovery.

A 1-month period or less if successfully treated. 1 No consistent reliable predictor of response has yet been identified. 2 The static failure to respond to treatment suggests that schizophrenia is a heterogeneous condition with different. Blunted affect alogia social withdrawal anhedonia and avolition. The label treatment resistance is used particularly to refer to patients whose positive symptoms of schizophrenia including delusions and hallucinations have not responded to treatment1-3 For definitions of positive and negative symptoms see Lambert and Castle 4 The focus on positive symptoms has arisen largely because other domains were either not clinically well recognised or.
 Source: thelancet.com
Source: thelancet.com
A 1-month period or less if successfully treated. Therefore IPAP suggests 2 forms of treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Thus the rigor of this study is. Delusions Hallucinations Disorganized speech eg frequent derailment or incoherence Grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior Negative symptoms ie diminished emotional expression or avolition. A 1-month period or less if successfully treated.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
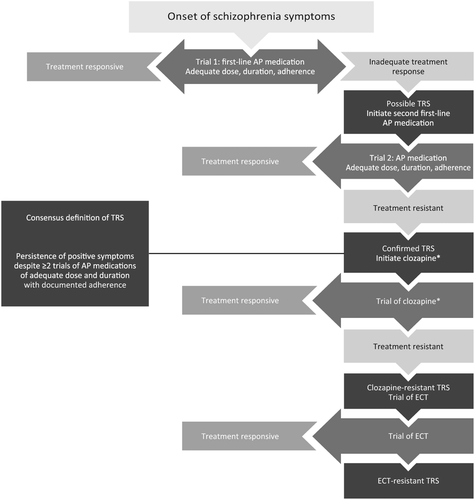
This study aimed to explore the potential immune mechanism of SSRI augmentation in the management of patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia assessing changes in IL-6 and CRP amounts. This was a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled. On a cross-sectional evaluation these patients with chronic schizophrenia were acutely ill and had high symptom levels as defined by a BPRS overall score 45 and an item score of 2 in hallucinations suspiciousness disorganization and unusual thought content. In contrast to treatment-responsive schizophrenia treatment-resistant schizophrenia appears to be characterised by a relatively normal dopamine system but an abnormal glutamate system and significant decreases in grey matter. A lthough antipsychotic medications have been the mainstay of treatment for schizophrenia approximately one-third of individuals with schizophrenia show a limited response to antipsychotic treatment 1 which has led to the term treatment-resistant schizophrenia TRS.
 Source: focus.psychiatryonline.org
Source: focus.psychiatryonline.org
In contrast to treatment-responsive schizophrenia treatment-resistant schizophrenia appears to be characterised by a relatively normal dopamine system but an abnormal glutamate system and significant decreases in grey matter. Delusions Hallucinations Disorganized speech eg frequent derailment or incoherence Grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior Negative symptoms ie diminished emotional expression or avolition. Treatment Resistant Schizophrenia General Principles Treatment resistant schizophrenia TRS is defined by an inadequate response to a succession of treatments Taylor and Duncan-McConnell 2000. Clozapine is the most effective antipsychotic in treating refractory schizophrenia but only about 50 of patients respond to treatment. While many definitions of TRS include failure of two different antipsychotics as a minimum criterion the wide variability in inclusion criteria has challenged the consistency and reproducibility of results from.
 Source: thelancet.com
Source: thelancet.com
Treatment-resistant schizophrenia TRS is broadly defined in clinical guidelines as an inadequate response in target schizophrenia symptoms often positive symptoms following treatment with two or more antipsychotic treatments of adequate dose and duration 2 6789. At least one of these must be delusions hallucinations or disorganized speech. Patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia showed a smaller reduction of negative symptoms after active vs sham tDCS. Kraepelinian schizophrenia with severe persistent cognitive deterioration Deficit schizophrenia with prominent primary negative symptoms. This was a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
While many definitions of TRS include failure of two different antipsychotics as a minimum criterion the wide variability in inclusion criteria has challenged the consistency and reproducibility of results from studies of TRS. While many definitions of TRS include failure of two different antipsychotics as a minimum criterion the wide variability in inclusion criteria has challenged the consistency and reproducibility of results from studies of TRS. This was a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled. Patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia showed a smaller reduction of negative symptoms after active vs sham tDCS. Clozapine is the most effective antipsychotic in treating refractory schizophrenia but only about 50 of patients respond to treatment.
 Source: psychiatrictimes.com
Source: psychiatrictimes.com
Therefore IPAP suggests 2 forms of treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Similar effects were observed for those with ultratreatment-resistant schizophrenia those who used clozapine and those who took higher haloperidol dose equivalents eTables 4 and 5 in Supplement 2. There is a phenomenon called burnout in older persons with schizophrenia in which positive symptoms improve or the psychosis burns out but the negative symptoms do not appear to. An inadequate response need not be restricted to the persistence of positive symptoms but this is the most common definition. While many definitions of TRS include failure of two different antipsychotics as a minimum criterion the wide variability in inclusion criteria has challenged the consistency and reproducibility of results from.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
While many definitions of TRS include failure of two different antipsychotics as a minimum criterion the wide variability in inclusion criteria has challenged the consistency and reproducibility of results from studies of TRS. Negative symptoms are characterised by deficits in normal behaviour which are categorised into five domains. This study aimed to explore the potential immune mechanism of SSRI augmentation in the management of patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia assessing changes in IL-6 and CRP amounts. Tentative evidence from a diverse range of research fields supports the idea that treatment-resistance may be a categorically distinct disorder. Treatment-resistant schizophrenia is a serious clinical problem.

Schizophrenia SCZ is a chronic relapsing and remitting disorder with a lifetime prevalence of 4 per 1000 persons. In consequence polypharmacy is frequently used in treatment-refractory cases addressing psychotic positive negative and cognitive symptoms treatment-emergent side effects caused by antipsychotics and comorbid depressive or obsessive-compulsive symptoms. Similar effects were observed for those with ultratreatment-resistant schizophrenia those who used clozapine and those who took higher haloperidol dose equivalents eTables 4 and 5 in Supplement 2. 2 The static failure to respond to treatment suggests that schizophrenia is a heterogeneous condition with different. However patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia often have persistent negative symptoms and prominent cognitive impairment.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title symptoms of treatment resistant schizophrenia by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





